The travel and tourism industry contributed to around 10.2 percent of the global GDP in 2016 (USD 7.6 Trillion) and created around 292 million jobs (1 in 10 jobs worldwide) annually, according to a report by the World Travel & Tourism Council. The industry's direct GDP contribution is expected to grow at around 3.9 percent annually over the next 10 years, touching around 11.4 percent of GDP and 380 million jobs by 2027.
However, the industry's growth has come with its share of challenges. Enhanced customer service at the lowest possible cost, bundling of bleisure, overcrowding of select destinations, and growth of personalized travel against mass travel are all creating margin pressures that are forcing travel businesses to re-evaluate their offerings and business models.
Seamless and personalized travel entails sharing and analyzing data across segments — from airports and airlines to hotels, restaurants, car rentals, railways and ground transportation providers. Travel businesses are fast realizing that delivering this at scale can only be possible through automation.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA), backed by analytics, Internet of Things, machine-learning, autonomous systems and Natural Language Processing, is thus seeing rapid adoption.
 Four Dimensions of RPA Adoption & Transformation
Four Dimensions of RPA Adoption & Transformation
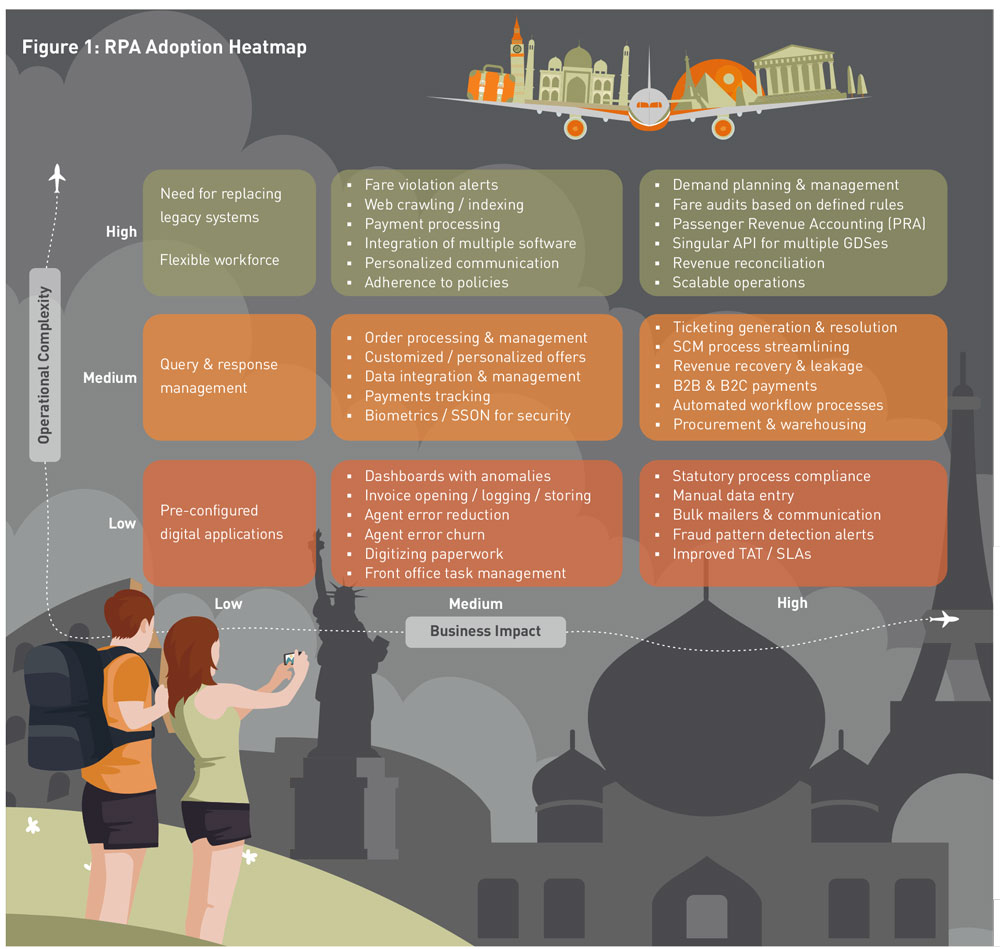
The scope for RPA implementation in travel can be understood through a services heatmap where we track business complexity on the Y-axis(high, medium and low) and business impact on the X-axis (high, medium and low) as shown in Figure 1. This heatmap can be replicated across most travel segments, but primarily applies to airlines, hotels / hospitality, airports, online travel agencies and travel management companies.
When we map the process-based offerings on both these axes, we find few operational tasks with low business impact. Effectively, all processes with a medium-to-high complexity and impact are ideal for RPA deployment, further strengthening the case for a broader RPA adoption in the travel industry.
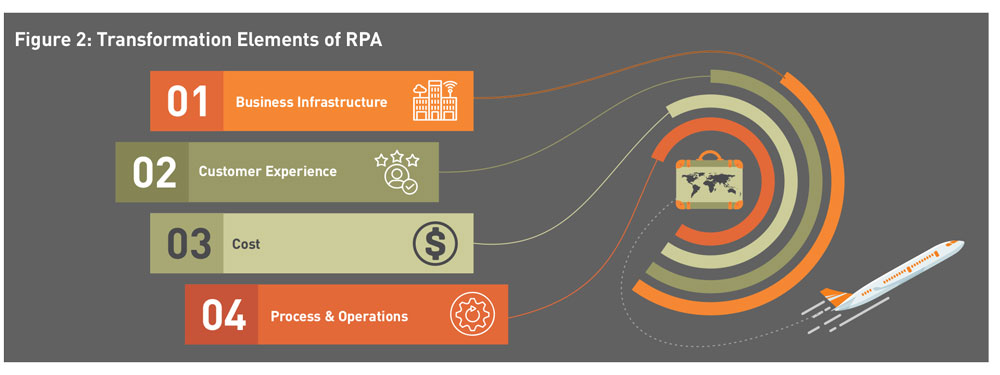
RPA can generate value for the travel industry by delivering transformation and optimization along four business dimensions: business infrastructure, customer experience, cost, and process and operations (Figure 2). Let's take a look at each of these dimensions and the transformation in detail.
 1. Business Infrastructure
1. Business Infrastructure
-
Integrating legacy systems and digital interfaces: RPA agents can access and pull information from the front-end of any system or application like human agents. This enables organizations to streamline the use of legacy systems / applications without heavy IT investments such as integration with a new system or platform, and coding or migrating data from an existing system to the cloud
-
Driving scalability and efficiency: Automation can replicate and scale processes for faster rollout as it can address the process lifecycle proactively: due diligence assessments, solution design, automation via user acceptance testing, refinement and data monitoring can be done while setting up a new workflow. Automated workflows across multiple departments and locations can help airlines and travel agencies rapidly raise the benchmark for process efficiency and scale
-
Ensuring high availability: RPA can ensure 100 percent system uptime in case of failures / disasters. Through Simple Network Management Protocol, RPA provides greater control, system backup and monitoring of devices. RPA helps retain system log information and reports, scans them for keywords and performance graphics that indicate problems, and automatically sets the restarting procedures into motion (for example, rerouting of network information or restoring backup from the cloud)
-
Automating business risk management: Since there are no human errors, and compliance steps are built into automated process activities, there is no risk of missing steps, entering incorrect information or sending information to wrong parties. All the activities are logged and traceable, and can be provisioned for reporting and investigation purposes.
 2. Customer Experience
2. Customer Experience
Improving customer satisfaction levels: By automating complex processes and systems, businesses can achieve better control, reduce unintended errors and delays, and ensure regulatory compliance. This helps improve customer satisfaction levels.
RPA can help employees focus on specific customer requirements rather than data reconciliation, filling forms or repetitive order processing.
It can help upload scanned documents, verify e-signatures and validate automatic approval or rejection recommendations, resulting in lower time to resolution for the end customer
-
Enhancing customer experience: Chatbots, infused with sentiment analysis technology, can detect customers' emotions via texts / calls, and help flag at-risk customers and escalate issues to call center agents.
This paves the path for delivering improved customer experience. From the Hello Hipmunk virtual travel agent to Hilton Hotels' Connie, the robotic concierge, and the mostly robotic staff of Henn-na Hotels in Japan, the travel industry is seeing many successful examples of enhanced customer experience through RPA
-
Using customer analytics to drive business outcomes: A combination of RPA algorithms along with Artificial Intelligence (AI), machine-learning and analytics can provide predictive insights in areas such as:
-
Customer mix and travel spends: Insights on customer mix in the near future, classified by demographic and their average spend per annum on travel can be a key driver for designing loyalty and promotional programs for airlines and hotels
-
Social media analytics: RPA can deliver insights on important booking sources (websites and travel integrators) along with customer profiles and top destination preferences by parsing texts, pages visited and destinations researched
-
Arresting revenue leakage: Airline and hotel transactions with different travel agencies need control and monitoring to ensure that there is no violation of fare rules at the time of issuing a ticket or processing refunds
Automated analytics can identify and alert companies about agencies that generate errors in real time so that revenue leakage can be addressed on-the-go
-
Harvesting Customer Relationship Management (CRM) analytics: Reservation changes, cancellations and refunds can all be analyzed at the macro and micro level to help build customer profiles and identify 'ideal' and 'most viable / lucrative' customers
 3. Cost
3. Cost
-
Reduced operational cost: RPA agents can accomplish multiple tasks without lags or errors, reducing re-work and freeing up human agents for more complex or sensitive tasks that require emotional intelligence or judgment. This can help drive higher margins and productivity per employee. Also, huge savings can be envisaged in the areas of training costs, reduced levels of attrition and thus reduced need to re-skill new hires, overheads and maintenance costs
-
Moving away from Full-time Equivalent (FTE) dependency: As customers seek to enhance value on their deals, businesses that stick to traditional FTE models have a higher chance of losing out in price wars. With the demand for gain-sharing / pay-as-per-use models growing by the day, automation can assist in raising the revenue per FTE and reduce costs significantly
 4. Process and Operations
4. Process and Operations
-
Process compliance and optimization: RPA solutions always follow a defined approach, with an ensured data log generated in the background. Statutory audits thus become far more efficient, with key accountability and authentication at the employee level made easily available.
Process activities can be consistently and predictably tracked along with time, and the number of steps to be followed can be reduced by identifying bottlenecks, measuring performance and building direct accountability
-
Increased security: RPA increases security with regard to sensitive tasks or confidential information. It also allows for exception management through the consistent application of rules, flags and red alerts, and adheres to control frameworks, thus reducing the error rate
-
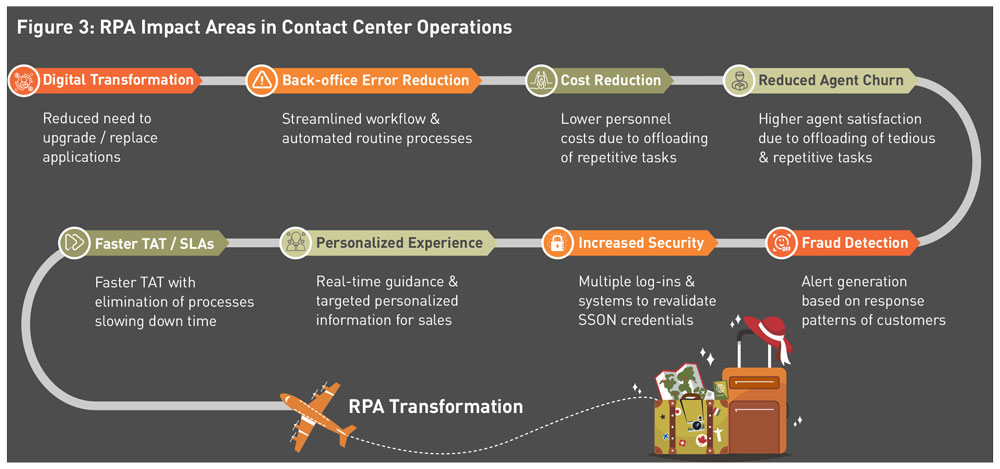
Operational transformation: As seen in the heatmap in Figure 1, most processes in the travel business qualify for RPA implementation. For example, contact center operations are one of the biggest beneficiaries of RPA in the travel industry.
Immediate benefits can be seen in areas such as reduced agent churn, enhanced outputs with improved service-level agreements, billing accuracy, claims resolution, and updated client profiles on the databases.
Figure 3 captures some key impact areas of RPA in contact center operations
RPA is thus set to drive strategic imperatives for at least the next two to three years across all consumer-driven businesses, especially travel. However, businesses should ensure proper due diligence in executing all level 1-2-3 processes with prospective vendors for successful implementation and tangible realization of RPA's benefits. Prioritizing the right impact area and implementing the right metrics to track benefits is equally important — be it infrastructure development, process improvement, cost reduction or customer engagement.
Explore WNS's insights on 5 air travel trends shaping the industry.